The Future of Indian Languages in a Globalized World
In an increasingly globalized world, Indian languages face both opportunities and challenges. Globalization brings about significant changes in communication, culture, and technology, impacting how languages are used, preserved, and developed. This article examines the future of Indian languages in the context of globalization, highlighting the dynamics of linguistic evolution, preservation efforts, and potential pathways for growth.

Impact of Globalization on Indian Languages
Increased Use of English
Globalization has led to the widespread use of English as a global lingua franca. In India, English has become prominent in business, technology, and higher education. This trend has influenced language use, with many Indians acquiring proficiency in English while sometimes using it as a primary or secondary language. The rise of English impacts the status and use of regional languages, often leading to concerns about language shift and erosion.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a dual role in the future of Indian languages. On one hand, digital platforms and tools facilitate the use and spread of languages through online content, social media, and mobile apps. On the other hand, the dominance of English in technology and digital interfaces can marginalize regional languages if not adequately addressed.
Cultural Exchange and Hybridization
Globalization promotes cultural exchange, leading to linguistic hybridization where languages borrow elements from one another. In India, this phenomenon can be observed in the blending of regional languages with English and other languages. While this can enrich linguistic expression, it also poses challenges to the purity and preservation of traditional languages.
Opportunities for Growth and Preservation
Promoting Multilingual Education
Multilingual education is crucial for the future of Indian languages. Integrating regional languages into the education system alongside English and other major languages can help maintain their relevance and use. Policies and programs that support bilingual or multilingual education promote linguistic diversity and ensure that students develop proficiency in both regional and global languages.
Digital and Media Innovations
Leveraging digital technology can support the growth and preservation of Indian languages. Developing digital content, such as websites, apps, and online courses, in regional languages helps to maintain their presence in the digital space. Media initiatives, including films, television shows, and social media content, can further promote and popularize regional languages.
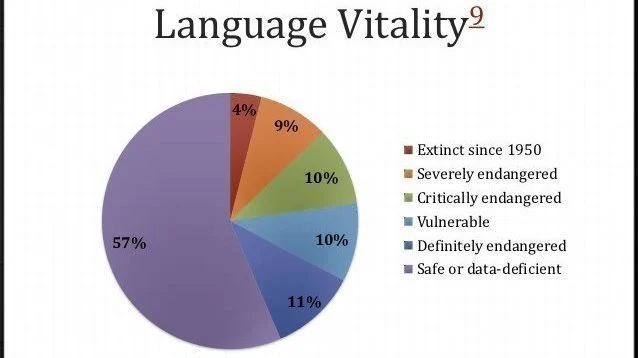
Language Revitalization Initiatives
Revitalization efforts are essential for preserving and fostering the growth of endangered and minority languages. Community-led initiatives, language documentation projects, and cultural programs contribute to the revitalization of languages. Collaboration with linguistic organizations and government bodies enhances these efforts, providing resources and support for language preservation.
Challenges and Solutions
Addressing Language Shift
Language shift, where speakers abandon their native languages in favor of more dominant ones, is a significant challenge. To counter this trend, it is important to create incentives for using regional languages in everyday life, such as in business, media, and public services. Promoting cultural pride and the value of linguistic heritage can also encourage language use among younger generations.
Bridging the Digital Divide
The digital divide can exacerbate linguistic inequalities, with some languages having limited online presence compared to others. Bridging this divide involves investing in digital infrastructure and creating resources that support the development and use of regional languages online. Encouraging tech companies to include regional languages in their products and services can help address this issue.
Balancing Tradition and Modernity
Balancing the preservation of traditional languages with the demands of modernity is a key challenge. Embracing language evolution while maintaining cultural heritage requires thoughtful strategies. Encouraging the use of regional languages in contemporary contexts, such as in new media and technology, helps to keep them relevant and vibrant.
Examples of Successful Language Initiatives
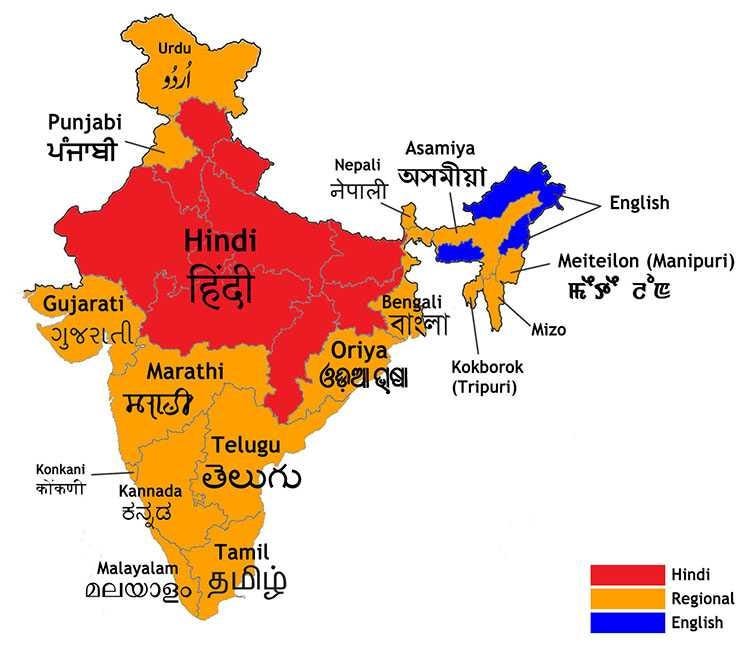
Regional Language Promotion
Successful initiatives in India, such as the promotion of languages like Tamil, Kannada, and Bengali in education and media, demonstrate effective strategies for language preservation and growth. These initiatives include language-specific educational programs, cultural festivals, and media productions that celebrate and sustain linguistic heritage.
Global Collaborations
International collaborations and programs aimed at language preservation and promotion provide valuable models for Indian languages. Efforts such as UNESCO’s linguistic projects and the work of global non-profits in language revitalization offer frameworks and support that can be adapted to the Indian context.
Conclusion
The future of Indian languages in a globalized world presents both challenges and opportunities. While globalization and technological advancements influence language dynamics, proactive strategies for multilingual education, digital innovation, and language revitalization can help preserve and promote linguistic diversity. Embracing the balance between tradition and modernity ensures that Indian languages continue to thrive and contribute to the rich cultural tapestry of the nation.